Book Appointment Now
Protecting Communities: The Role of the BCG Vaccine in Preventing Tuberculosis
- On
- InMarine
Understanding Tuberculosis (TB)
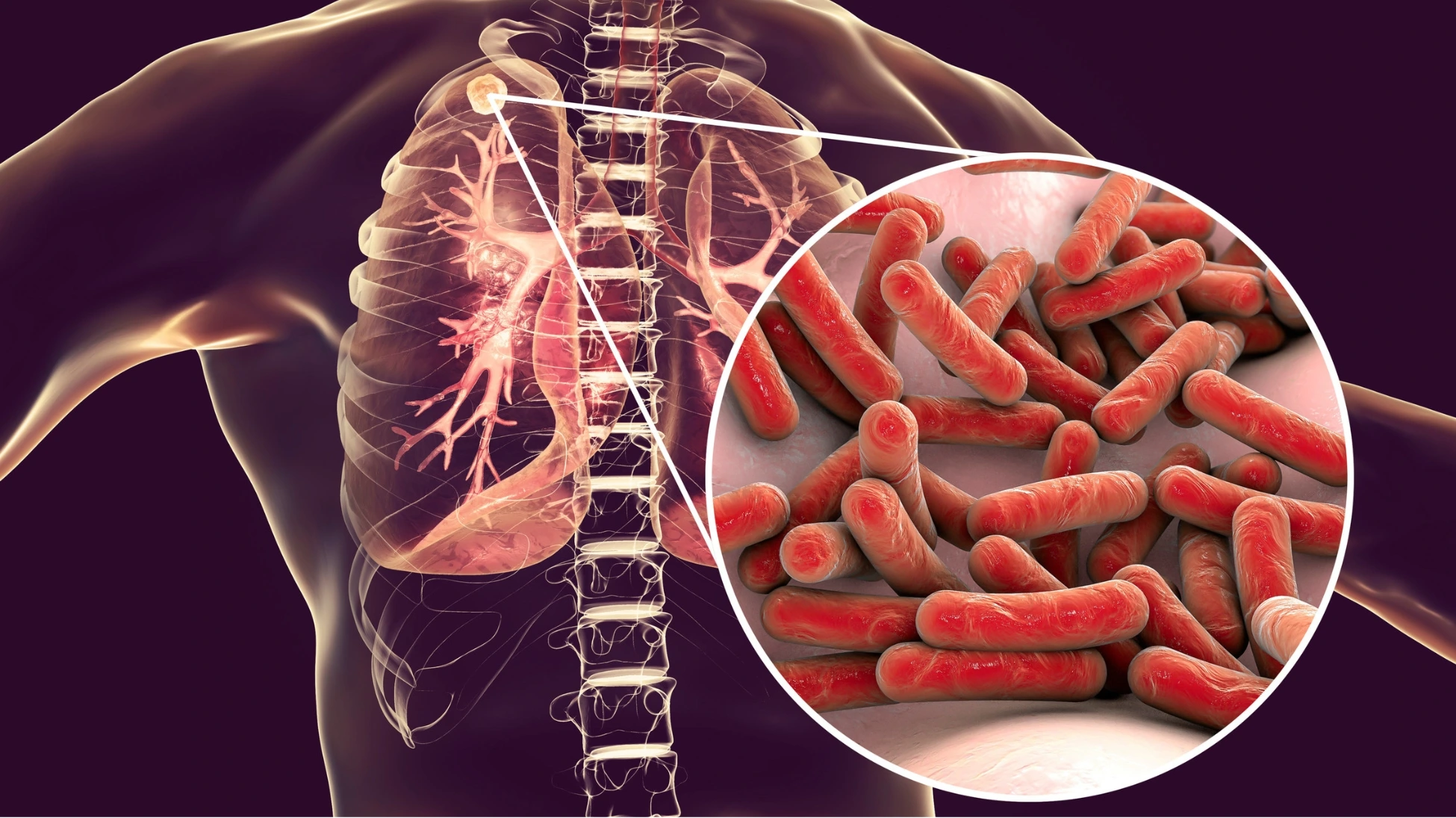
Tuberculosis (TB) remains one of the world’s deadliest infectious diseases, claiming over a million lives each year. Caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria, TB primarily affects the lungs but can also spread to other parts of the body. Despite being preventable and treatable, TB continues to pose significant public health challenges, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.
TB is an airborne disease, meaning it spreads when an infected person coughs or sneezes, releasing bacteria into the air. While not everyone exposed to TB becomes ill, those with weakened immune systems are at greater risk. This makes prevention efforts, including vaccination, critical in reducing TB’s global impact.
The Importance of World Tuberculosis Day
World Tuberculosis Day, observed annually on March 24th, serves as a reminder of the global efforts needed to eliminate TB. It commemorates the discovery of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis by Dr. Robert Koch in 1882, which paved the way for advancements in diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
This day is also an opportunity to raise awareness about the continued prevalence of TB, especially in underserved communities. Governments, health organizations, and advocacy groups often use World TB Day to promote screening programs, vaccination drives, and treatment accessibility.
What is the BCG Vaccine?
The Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine is the most commonly used vaccine for TB prevention. Developed from a weakened strain of Mycobacterium bovis, the BCG vaccine has been used for over a century and is primarily administered to infants in countries with high TB prevalence.
How Does the BCG Vaccine Work?
The vaccine stimulates the immune system to recognize and respond to TB bacteria. While it does not provide complete immunity, the BCG vaccine is highly effective in preventing severe forms of TB, particularly in children. It significantly reduces the risk of TB meningitis and disseminated TB, which are life-threatening forms of the disease.
The vaccine is usually given as a single dose through an intradermal injection, typically in the upper arm. A small raised bump may form at the injection site, often leaving a minor scar. This is a normal reaction and a sign that the vaccine is working.
Who Should Receive the BCG Vaccine?
- Infants and Children: In countries with high TB rates, BCG vaccination is typically part of routine immunization programs.
- Healthcare Workers: Individuals frequently exposed to TB patients may receive the vaccine to reduce their risk of infection.
- Travelers to High-Risk Areas: People traveling to regions with a high TB burden may consider getting vaccinated, especially if they will have prolonged contact with local communities.
In some low-prevalence countries, BCG vaccination is no longer part of routine immunization programs due to the low risk of TB. Instead, targeted vaccination may be recommended for specific groups at higher risk of exposure.
Effectiveness and Limitations
While the BCG vaccine is effective in preventing severe TB in children, its protection against pulmonary TB in adults varies. Research is ongoing to develop more effective TB vaccines, but BCG remains a crucial tool in global TB control efforts.
Factors influencing the vaccine’s effectiveness include the individual’s age, health status, and the prevalence of TB in their community. Additionally, the vaccine’s protection tends to wane over time, which is why regular TB screenings are still recommended for high-risk individuals.
Recognizing TB Symptoms and Seeking Early Diagnosis
Early detection is key to managing and preventing the spread of TB. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent cough lasting more than three weeks
- Chest pain
- Coughing up blood
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fever and night sweats
TB symptoms may develop gradually and can be mistaken for other illnesses. Anyone experiencing these symptoms, especially in areas with a high incidence of TB, should seek medical advice promptly. Diagnostic tests like chest X-rays, sputum tests, and TB skin tests can confirm the presence of the infection.
Preventing the Spread of TB
Preventing TB transmission requires a combination of vaccination, early diagnosis, and proper treatment. In addition to the BCG vaccine, individuals can protect themselves and others by:
- Practicing good respiratory hygiene (covering coughs and sneezes)
- Ensuring adequate ventilation in living and working spaces
- Wearing masks in crowded or high-risk areas
- Taking prescribed TB medications as directed
Communities can also benefit from public health initiatives that offer free or affordable TB screenings, vaccinations, and treatment programs.
Accessing TB Care Through MCMI and Ship to Shore Medical Assist (SSMA)
Navigating TB prevention, screening, and treatment can be overwhelming, but support is available. Medical Case Management International (MCMI) and Ship to Shore Medical Assist (SSMA) help individuals access the care they need—on land and at sea.
- MCMI serves non-maritime clients, including families, employees, and travelers in land-based industries.
- SSMA specializes in healthcare support for maritime clients, including seafarers and vessel operators.
How MCMI and SSMA Support Your Health Journey
Whether you’re looking for BCG vaccination, TB screening, or care coordination, MCMI and SSMA connect you with trusted healthcare providers and guide you through each step of the process. SSMA, the first post-PEME clinic in the Philippines accredited by the North of England P&I Association, brings decades of expertise in maritime medical care. MCMI ensures non-maritime clients receive individualized case management wherever they are.
Benefits of Partnering with MCMI and SSMA
- Seamless Access to Care: Get connected to qualified providers for TB diagnosis and treatment.
- Preventive Healthcare: Receive timely BCG vaccinations and regular screenings.
- Continuity of Care: From initial consults to follow-ups, your care journey is fully supported.
- Industry-Specific Support: MCMI for land-based clients, SSMA for those in the maritime sector.
Taking Action Against TB
TB prevention requires a shared effort. Here’s how you can help protect yourself and others:
- Get Vaccinated: Make sure children receive the BCG vaccine, especially in high-risk areas.
- Stay Informed: Learn the symptoms of TB and educate others about prevention.
- Practice Hygiene: Good ventilation, cough etiquette, and mask use reduce the risk of transmission.
- Seek Early Care: Don’t delay medical attention if symptoms appear.

If you or a loved one needs help with TB vaccination, screening, or treatment coordination, MCMI and SSMA are here to support you—wherever you are.
